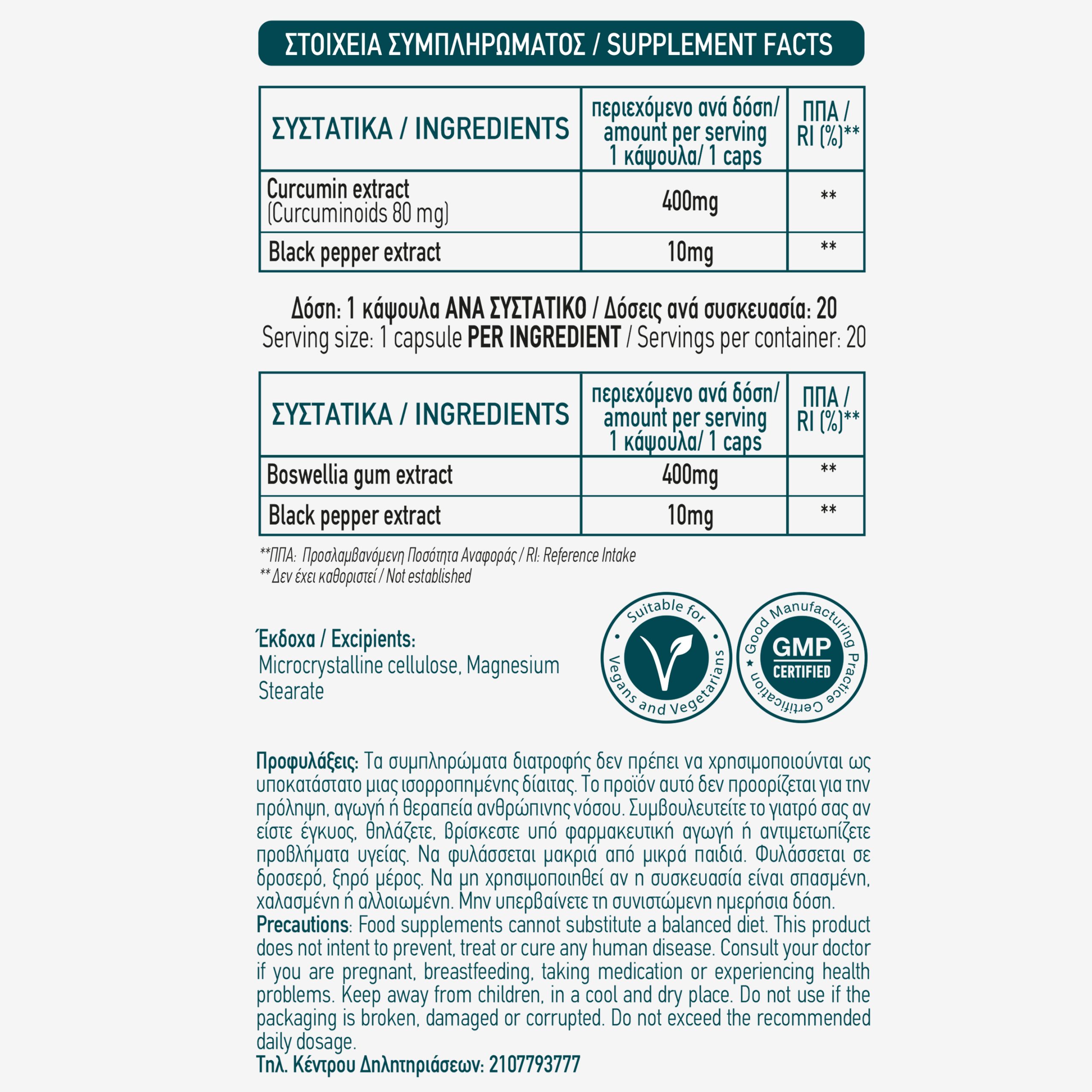
Relief
Natural food supplement with an innovative combination of highly bioavailable curcumin and boswellia plant resin:
- With strong pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory action.
- Does not irritate the gastric environment or cause stomach ulcers.
- Does not affect liver & kidney function.
- Helps to treat inflammatory pain:
- Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Musculoskeletal pains & Joint pains
- Dysmenorrhea
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Asthma
Proven Health Benefits of Turmeric and Curcumin
Curcumin may have anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidant, and other benefits. Turmeric may be the most effective nutritional supplement in existence. Many high-quality studies show that curcumin has major benefits for your body and brain.
What are turmeric and curcumin?
Turmeric has been used in India for thousands of years as both a spice and medicinal herb. Recently, science has started to back up traditional claims that turmeric contains compounds with medicinal properties (1). These compounds are called curcuminoids. The most important of them is curcumin. Curcumin is the main active ingredient in turmeric. It has powerful anti-inflammatory effects and is a very strong antioxidant. Curcumin is poorly absorbed into our bloodstream. In order to experience the full effects of curcumin, its bioavailability (the rate at which your body absorbs a substance) needs to improve (3). It helps to consume it with black pepper, which contains piperine. Piperine is a natural substance that enhances the absorption of curcumin by 2,000% (4). In fact, the best curcumin supplements, like relief, contain piperine, and this makes them substantially more effective.
Proven Health Benefits of Curcumin
1. Curcumin is a natural anti-inflammatory compound
Chronic inflammation contributes to some common health conditions, such as:
- heart disease
- cancer
- metabolic syndrome
- Alzheimer’s disease
- various degenerative conditions
Curcumin can suppress many molecules known to play major roles in inflammation, but its bioavailability needs to be enhanced.
2. Turmeric can increase the antioxidant capacity of the body
Oxidative damage is believed to be one of the mechanisms behind aging and many diseases. It involves free radicals, highly reactive molecules with unpaired electrons. The main reason antioxidants are so beneficial is that they protect your body from free radicals. Curcumin is a potent antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals due to its chemical structure (11). In addition, animal and cellular studies suggest that curcumin may block the action of free radicals and may stimulate the action of other antioxidants (12).
3. Turmeric as Pain Relief
In clinical studies, turmeric’s anti-inflammatory action appears to help improve rheumatoid arthritis, post-operative inflammation, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and stomach ulcers.
Arthritis patients respond well to curcumin supplements Arthritis is a common disorder characterized by joint inflammation. Many studies show that curcumin can help treat symptoms of arthritis and is, in some cases, more effective than anti-inflammatory drugs.
4. Curcumin may help fight various degenerative processes in your brain
Curcumin may boost levels of the brain hormone BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), which increases the growth of new neurons. Many common brain disorders have been linked to decreased levels of BDNF protein, including depression and Alzheimer’s disease (15, 16). Interestingly, studies have found that curcumin may increase brain levels of BDNF (17, 18). By doing this, it may be effective in delaying or even reversing many brain diseases and age-related decreases in brain function. It may also help improve memory and attention, which seems logical given its effects on BDNF levels (21).
5. Curcumin may lower risk of heart disease
Heart disease is the number one cause of death in the world (22). Curcumin may help reverse many steps in the heart disease process (23, 24). Perhaps the main benefit of curcumin when it comes to heart disease is improving the function of the endothelium, the lining of your blood vessels (25). The endothelial dysfunction is a major driver of heart disease. Several studies suggest that curcumin can lead to improvements in heart health (27, 28). In addition, curcumin can help reduce inflammation and oxidation, which can play a role in heart disease. 121 patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery, were assigned either to a placebo or curcumin a few days before and after the surgery. The curcumin group had a 65% decreased risk of experiencing a heart attack in the hospital (30).
6. Turmeric may help prevent cancer
Curcumin may lead to several changes on the molecular level that may help prevent and perhaps even treat cancer. Studies have shown that it can (33, 34):
- contribute to the death of cancer cells
- reduce angiogenesis (growth of new blood vessels in tumors)
- reduce metastasis (spread of cancer)
7. Curcumin may be useful in treating Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia and may contribute to up 70% of dementia cases.
Curcumin can cross the blood-brain barrier and has been shown to lead to various improvements in the pathological process of Alzheimer’s disease.
8. Curcumin has benefits against depression
A study in 60 people with depression showed that curcumin was as effective as Prozac in alleviating symptoms of the condition.
9. Curcumin may help delay aging and fight age-related chronic disease
Due to its many positive health effects, such as the potential to prevent heart disease, Alzheimer’s, and cancer, curcumin may aid longevity.
In summary
Curcumin has many scientifically proven health benefits, such as the potential to improve heart health and prevent Alzheimer’s and cancer.
It’s a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant. It may also help improve symptoms of depression and arthritis.
Piperine increases curcumin’s scarce bioavailability by as much as 2,000%.
Proven Health Benefits of Boswellia serrata
Overview
Boswellia, also known as Indian frankincense, is an herbal extract taken from the Boswellia serrata tree. The resin made from boswellia extract has been used for centuries in Asian and African altrenative medicine. It’s believed to treat chronic inflammatory illnesses as well as a number of other health conditions.
Studies show that boswellia may reduce inflammation and may be useful in treating the following conditions:
- osteoarthritis (OA)
- rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- asthma
- inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Because boswellia is an effective anti-inflammatory, it can be an effective painkiller and may prevent the loss of cartilage.
How boswellia works
Some research shows that boswellic acid can prevent the formation of leukotrienes in the body. Leukotrienes are molecules that have been identified as a cause of inflammation. They may trigger asthma symptoms. Four acids in boswellia resin contribute to the herb’s anti-inflammatory properties. These acids inhibit 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO), an enzyme that produces leukotriene. Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) is thought to be the most powerful of the four boswellic acids.
On OA
On RA
On IBD
On asthma
On cancer
Boswellic acids act in a number of ways that may inhibit cancer growth. Boswellic acids have been shown to prevent certain enzymes from negatively affecting DNA. Studies have also found that boswellia extract may have a positive role in breast cancel, in malignant leukemia and brain cancer. Studies continue and highlight the anti-cancer activity of boswellia.
Dosage
Side effects
Boswellia may stimulate blood flow in the uterus and pelvis. Therefore it can accelerate menstrual flow.
Other possible side effects of boswellia include:
- nausea
- acid reflux
- diarrhea
- skin rashes
Boswellia extract may also interact with medications, including ibuprofen, aspirin, and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).